
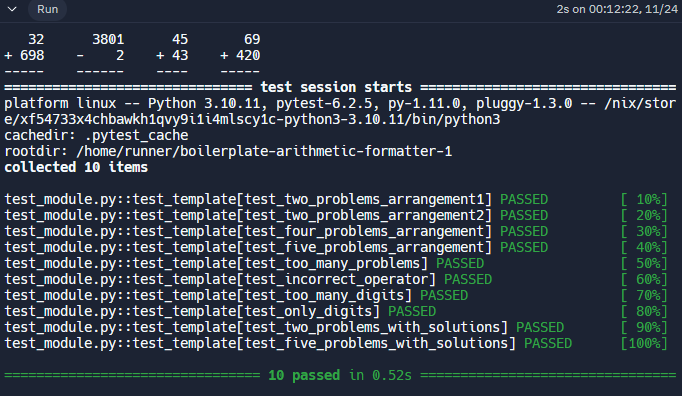
Arithmetic Formatter
Scientific Computing with Python Projects – Arithmetic Formatter | Learn | freeCodeCamp.org
from re import error
def arithmetic_arranger(problems, show_answers=False):
# Check if the number of problems is more than 5
if len(problems) > 5:
return "Error: Too many problems."
arranged_problems = ""
line1 = ""
line2 = ""
dashes = ""
answers = ""
for problem in problems:
# Split the problem into operands and operator
operand1, operator, operand2 = problem.split()
# Check if the operands are numeric
if not operand1.isdigit() or not operand2.isdigit():
return "Error: Numbers must only contain digits."
# Check if the operator is valid
if operator not in ['+', '-']:
return "Error: Operator must be '+' or '-'."
# Check if numbers are more than four digits
if len(operand1) > 4 or len(operand2) > 4:
return "Error: Numbers cannot be more than four digits."
# Find the length of the longer operand
max_length = max(len(operand1), len(operand2)) + 2
# Create the formatted expressions
line1 += operand1.rjust(max_length) + " "
line2 += operator + operand2.rjust(max_length - 1) + " "
dashes += '-' * max_length + " "
# Calculate the answer if show_answers is True
if show_answers:
if operator == '+':
result = str(int(operand1) + int(operand2))
else:
result = str(int(operand1) - int(operand2))
answers += result.rjust(max_length) + " "
# Remove the trailing whitespace
arranged_problems = f"{line1.rstrip()}\n{line2.rstrip()}\n{dashes.rstrip()}"
if show_answers:
arranged_problems += f"\n{answers.rstrip()}"
return arranged_problems
Time Calculator
Scientific Computing with Python Projects – Time Calculator | Learn | freeCodeCamp.org
def add_time(start_time, duration, start_day=None):
# Parse start time
start_time, am_pm = start_time.split()
start_hour, start_minute = map(int, start_time.split(':'))
# Parse duration time
duration_hour, duration_minute = map(int, duration.split(':'))
# Convert start time to 24-hour format
if am_pm == "PM":
start_hour += 12
# Calculate total minutes
total_minutes = start_hour * 60 + start_minute + duration_hour * 60 + duration_minute
# Calculate new time and day
new_hour = total_minutes // 60 % 24
new_minute = total_minutes % 60
# Determine AM or PM for the new time
new_am_pm = "AM" if new_hour < 12 else "PM"
# Adjust new hour to 12-hour format
if new_hour >= 12:
new_am_pm = "PM" if new_hour >= 12 else "AM"
new_hour = new_hour % 12
# Handling midnight
if new_hour == 0:
new_hour = 12
# Days later calculation
days_later = total_minutes // (24 * 60)
# Day of the week calculation
if start_day:
days_of_week = ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"]
start_day = start_day.lower().capitalize()
start_day_index = days_of_week.index(start_day)
new_day_index = (start_day_index + days_later) % 7
new_day = days_of_week[new_day_index]
# Building the result string
result = f"{new_hour}:{new_minute:02d} {new_am_pm}"
if start_day:
result += f", {new_day}"
if days_later == 1:
result += " (next day)"
elif days_later > 1:
result += f" ({days_later} days later)"
return result
# Examples
# print(add_time("3:00 PM", "3:10"))
# print(add_time("11:30 AM", "2:32", "Monday"))
# print(add_time("11:43 AM", "00:20"))
# print(add_time("10:10 PM", "3:30"))
# print(add_time("11:43 PM", "24:20", "tueSday"))
# print(add_time("6:30 PM", "205:12"))
Budget App
Scientific Computing with Python Projects – Budget App | Learn | freeCodeCamp.org
def truncate(n):
multiplier = 10
return int(n * multiplier) / multiplier
def getTotals(categories):
total = 0
breakdown = []
for category in categories:
total += category.get_withdrawls()
breakdown.append(category.get_withdrawls())
rounded = list(map(lambda x: truncate(x/total), breakdown))
return rounded
def create_spend_chart(categories):
res = "Percentage spent by category\n"
i = 100
totals = getTotals(categories)
while i >= 0:
cat_spaces = " "
for total in totals:
if total * 100 >= i:
cat_spaces += "o "
else:
cat_spaces += " "
res+= str(i).rjust(3) + "|" + cat_spaces + ("\n")
i-=10
dashes = "-" + "---"*len(categories)
names = []
x_axis = ""
for category in categories:
names.append(category.name)
maxi = max(names, key=len)
for x in range(len(maxi)):
nameStr = ' '
for name in names:
if x >= len(name):
nameStr += " "
else:
nameStr += name[x] + " "
if(x != len(maxi) -1 ):
nameStr += '\n'
x_axis += nameStr
res+= dashes.rjust(len(dashes)+4) + "\n" + x_axis
return res
class Category:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.ledger = list()
def __str__(self):
title = f"{self.name:*^30}\n"
items = ""
total = 0
for item in self.ledger:
items += f"{item['description'][0:23]:23}" + f"{item['amount']:>7.2f}" + '\n'
total += item['amount']
output = title + items + "Total: " + str(total)
return output
def deposit(self, amount, description=""):
self.ledger.append({"amount": amount, "description": description})
def withdraw(self, amount, description=""):
if(self.check_funds(amount)):
self.ledger.append({"amount": -amount, "description": description})
return True
return False
def get_balance(self):
total_cash = 0
for item in self.ledger:
total_cash += item["amount"]
return total_cash
def transfer(self, amount, category):
if(self.check_funds(amount)):
self.withdraw(amount,"Transfer to " + category.name)
category.deposit(amount, "Transfer from " + self.name)
return True
return False
def check_funds(self, amount):
if(self.get_balance() >= amount):
return True
return False
### Category method
def get_withdrawls(self):
total = 0
for item in self.ledger:
if item["amount"] < 0:
total+= item["amount"]
return total
# Example usage:
# food_category = Category("Food")
# clothing_category = Category("Clothing")
# entertainment_category = Category("Entertainment")
# food_category.deposit(900, "deposit")
# food_category.withdraw(45.67, "milk, cereal, eggs, bacon, bread")
# food_category.transfer(20, entertainment_category)
# print(food_category)
# print(create_spend_chart([food_category, clothing_category, entertainment_category]))
Polygon Area Calculator
Scientific Computing with Python Projects – Polygon Area Calculator | Learn | freeCodeCamp.org
class Rectangle:
def __init__(self, width, height):
self.width = width
self.height = height
def __str__(self): # String interpulation
return f'Rectangle(width={self.width}, height={self.height})'
def set_width(self, width):
self.width = width
def set_height(self, height):
self.height = height
def get_picture(self):
if(self.width > 50 or self.height > 50):
return "Too big for picture."
string = (("*" * self.width) + "\n") * self.height
return string
def get_area(self):
return self.width * self.height
def get_perimeter(self):
return 2 * self.width + 2 * self.height
def get_diagonal(self):
return ((self.width ** 2 + self.height ** 2) ** .5)
def get_amount_inside(self, shape):
return int(self.get_area() / shape.get_area())
class Square(Rectangle):
def __init__(self, side):
self.width = side
self.height = side
def __str__(self):
return f'Square(side={self.width})'
def set_side(self, side):
self.width = side
self.height = side
# I,m so tired....Probability Calculator
Scientific Computing with Python Projects – Probability Calculator | Learn | freeCodeCamp.org
import copy
import random
from collections import Counter
class Hat:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.contents = []
for color, count in kwargs.items():
self.contents.extend([color] * count)
def __str__(self):
return ', '.join(self.contents)
def get_contents(self):
return self.contents
def draw(self, number):
if number >= len(self.contents):
return self.contents
return [self.contents.pop(random.choice(range(len(self.contents)))) for _ in range(number)]
def experiment(hat, expected_balls, num_balls_drawn, num_experiments):
count = 0
for _ in range(num_experiments):
expected_copy = Counter(expected_balls)
hat_copy = copy.deepcopy(hat)
colors_gotten = hat_copy.draw(num_balls_drawn)
colors_gotten_count = Counter(colors_gotten)
# Check if expected colors are a subset of the drawn colors
if all(colors_gotten_count[color] >= expected_copy[color] for color in expected_copy):
count += 1
return count / num_experiments
# AHhHhHhH

0 Comments